304 Stainless Steel Properties: SS304 Composition, Density, Yield Strength, Thermal Conductivity, Hardness, Modulus of Elasticity
AISI 304 Stainless Steel (UNS S30400)
AISI 304 stainless steel (UNS S30400) is the most commonly used material in stainless steels, and is usually purchased in an annealed or cold worked state. Because SS304 contains 18% chromium (Cr) and 8% nickel (Ni), it’s also known as 18/8 stainless steel. Type 304 has good processability, weldability, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties, good hot workability such as stamping and bending, and no heat treatment hardening. SS 304 is widely used in the industrial use, furniture decoration, food and medical industry, etc.
AISI 304L is the low carbon version of 304 stainless steel, AISI 303 is a free-machining steel, basically a variant of SS304, which increases the phosphorus (P) and sulfur (S) content and improves the machinability. AISI 316 is better than 304 in certain properties, corrosion resistance and heat resistance, etc. For more information, please check 304 vs 304L stainless steel and 304 vs 316 stainless steel.
SS 304 Stainless Steel Properties
The following datasheet and specification show SS 304 stainless steel properties including physical properties and mechanical properties.
Chemical Composition
Type 304 grade stainless steel composition is given in table below.
Datasheet 1, AISI 304 stainless steel composition
| Chemical Composition, % | ||||||||||
| ASTM | AISI (UNS) | C, ≤ | Si, ≤ | Mn, ≤ | P, ≤ | S, ≤ | Cr | Ni | N, ≤ | Product |
| ASTM A240/A240M | 304 (UNS S30400) | 0.07 | 0.75 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 17.5-19.5 | 8.0-10.5 | 0.10 | Plate, Sheet, and Strip |
| ASTM A276/276M | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | – | Bars and Shapes | |
SS304 Stainless Steel Mechanical Properties
Datasheet-2, the tables below list SS304 material mechanical properties including yield strength, tensile strength, elongation and hardness, etc.
| Mechanical Properties, data are for 25.4 mm (1 in.) diameter bar | ||||||
| Steel (UNS) | Tensile strength, MPa (ksi) | Yield strength, MPa (ksi) | Elongation in 50 mm (2 in.), % ≥ | Reduction in area (%) | Hardness (HB) | Condition |
| AISI 304 (UNS S30400) | 585 (85) | 235 (34) | 60 | 70 | 149 | Annealed bar |
| 690 (100) | 415 (60) | 45 | 212 | Annealed and cold drawn | ||
| 860 (125) | 655 (95) | 25 | 275 | Cold drawn high tensile | ||
Datasheet 3, ASTM 304 Stainless Steel Properties – Mechanical Properties
| Mechanical Properties | |||||||||
| ASTM Type | AISI (UNS) | Tensile Strength, MPa (ksi) | 0.2% Yield Strength, MPa (ksi) | Elongation in 50 mm (2 in.), % ≥ | Reduction of Area, %, ≥ | Brinell Hardness (HBW) ≤ | Rockwell Hardness (HRBW) ≤ | Product | Condition |
| ASTM A240/A240M | 304 (UNS S30400) | 515 (75) | 205 (30) | 40 | – | 201 | 92 | Plate, Sheet, and Strip | – |
| ASTM A276A/276M | 515 (75) | 205 (30) | 40 | 50 | – | – | Bars and Shapes | Hot finished | |
| 620 (90) | 310 (45) | 30 | 40 | – | – | Cold finished, Dia ≤ 12.7mm (0.5 in) | |||
| 515 (75) | 205 (30) | 30 | 40 | – | – | Cold finished, Dia. > 12.7mm (0.5 in) | |||
Data comes from professional, authoritative and trustworthy ASTM standards.
Physical Properties
Datasheet 4, SS304 physical properties
- 1 g/cm3 = 1 kg/dm3 = 1000 kg/m3;
- 1 μΩ·m = 1 Ω·mm²/m
- 1 GPa = 1 kN/mm2
| Physical Properties | |
| Density, g/cm3 (lbs/in3) | 7.93 (0.286) |
| Melting point, °C (°F) | 1398-1454 (2550-2650) |
| Magnetic in annealed condition | No |
| Magnetic permeability | 1.02 (Approximate) |
| Specific heat capacity, J/(Kg·K) | 500 at 0-100 °C (32-212 °F) |
| Electrical resistivity, μΩ·m | 0.73 at 20 °C (68 °F) |
| Modulus of elasticity (Elastic modulus), GPa (psi) | 193 (28×106) |
| Thermal diffusivity, mm2/s | 3.84 at 20-100 °C (68-212) |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | 16.3 at 100 °C (212 °F) |
| 21.5 at 500 °C (932 °F) | |
| Mean coefficient of thermal expansion, (10-6/K) | 17.2 at 0-100 °C (32-212 °F) |
| 17.8 at 0-315 °C (32-600 °F) | |
| 18.4 at 0-538 °C (32-1000 °F) | |
Magnetic Properties
Type 304 stainless steel is not magnetic, but may be slightly magnetic after cold working.
Heat Resistance
Maximum service temperature in air
- Intermittent service temperature: 870 °C (1600 °F);
- Continuous service temperature: 925 °C (1700 °F);
Sensitization occurs when type 304 austenitic stainless steel is heated between 425 and 815 °C (800-1500 °F). Carbon and chromium combine to form chromium carbide, which precipitates at the crystal boundary, so the Cr content near the grain boundary is greatly reduced, and becomes a Cr-depleted region. Therefore, its corrosion resistance is lowered.
In order to prevent sensitization, the following methods can be used for AISI 304 stainless steel:
- Rapidly passing the sensitized temperature range 425-815 °C (800-1500 °F), thus Cr does not have enough time to combine with C, and it is impossible to precipitate chromium carbide.
- The sensitized stainless steel is reheated to a temperature 1040-1065 °C (1900-1950 °F) sufficient to decompose the chromium carbide, and then rapidly cooled (water quenching if possible) to make the chromium carbide less likely to precipitate.
- Use ultra-low carbon austenitic stainless steels, such as 304L and 316L, can reduce the formation of chromium carbide and reduce the probability of chromium-depleted envelope.
Heat Treating 304 Stainless Steel
The following is the heat treating 304 stainless steel, such as annealing, forging, hardening, stress relieving, etc.
Annealing (Solution Annealing)
Type 304 stainless steel annealing temperature range is 1010-1065 °C (1850-1950 °F),1040 °C (1900 °F) is recommended and then rapidly cooled.
Before annealing, the surface should be carefully cleaned, and to prevent the formation of an oxide layer during the annealing process, vacuum, hydrogen or inert gas protection must be used.
Forging Temperature
Type 304 stainless steel typical forging temperature is 925-1260 °C (1700-2300 °F).
Hardening
AISI SAE ASTM 304 stainless steel can’t be hardened by heat treatment but can be hardened by cold working.
Stress Relieving Temperature
When the weldment is not suitable for full annealing, the residual stress of SS 304 grade stainless steel can be moderately reduced below 450 °C (840 °F).
Cold Working
SS304 is suitable for cold working operations including cold heading, cold drawing, cold extrusion and cold riveting, but it is more difficult than cold working of carbon steel.
Machining
Type 304 stainless steel is more difficult to machine than carbon steel and low alloy steel because of its higher strength and higher work hardening rate. Therefore, more power and lower processing speed are required, resulting in shortened tool life and difficulty in obtaining a smooth surface.
Welding
SS 304 has excellent welding performance and does not require preheating, but requires similar filler material composition but high alloy content. Ensure that the weld contains 5-10% ferrite during welding to avoid cracking of the weld. Reduce the carbon content, such as using 304L, stabilized stainless, or adding niobium (Nb), to avoid weld corrosion. SS 304 may require subsequent reannealing after soldering or heat treatment to achieve optimum corrosion resistance, softness and ductility. Because intergranular corrosive chromium carbide is dissolved during the annealing process.
Postweld heat treatment: 949-1149 °C (1740-2100 °F) if undertaken, or stress relieve below 649 °C (1200 °F) to avoid weld corrosion.
Corrosion Resistance
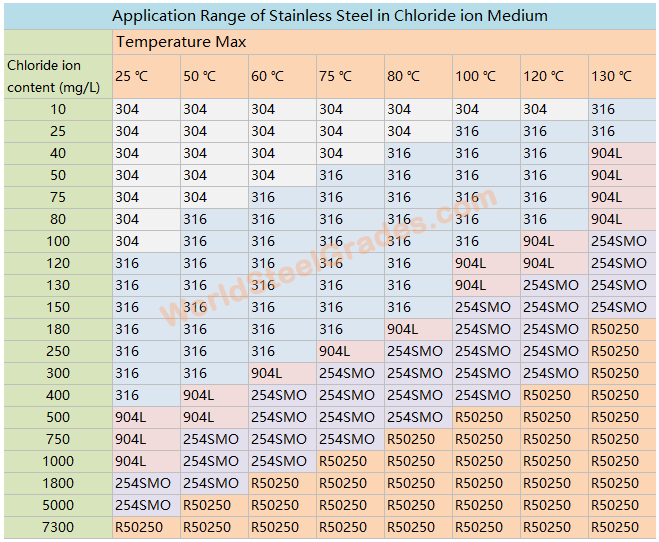
The reason why AISI 304 grade stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance in the atmosphere is due to the formation of a chromium passivation film on its surface. But when SS304 is in a warm chloride environment, the corrosion is even faster than non-alloy mild steel. Below is the application range of stainless steel in chloride ion medium for reference.
Examples of ASTM 304 stainless steel rust environment: Sea water, sea wind, salt, perspiration, etc.
Applications
AISI 304 stainless steel is widely used in petroleum & chemical industry, metallurgical machinery, aerospace industry, food processing equipment, instruments, household appliances and hardware manufacturing industries.
SS304 material is made into a great many intermediate products such as steel sheet & plate, steel tube & pipe, steel bar & flat, rod & wire, etc.
Final products such as all kinds of kitchen ware, tableware, medical device, machinery and parts, wire mesh, filters, architectural and decorative products, etc.
AISI 304 Equivalent Grade
ASTM type 304 stainless steel equivalent material is listed in the table below, including ISO, European EN (Germany DIN, British BSi, France NF…), Japanese JIS and Chinese GB standard (For reference).
Notes:
- DIN 17440 has been replaced by DIN EN 10088-2.
- Chinese stainless steel grade 0Cr18Ni9 is an old designation, and has been replaced by the new name 06Cr19Ni10.
- ASTM A240/A240M – Standard Specification for Chromium and Chromium-Nickel SS Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and for General Applications.
- ASTM A276/A276M – Standard Specification for SS Bars and Shapes.
- JIS G4304 :2005 – Hot rolled stainless steel plate, steel sheet and steel strip.
- GB/T 1220: 2007 – Stainless steel bars.
- GB/T 3280: 2015 – Cold rolled stainless steel plate, steel sheet and steel strip.
| AISI 304 Equivalent Grade | |||||||||||||||
| US | European | Germany | Britain (UK) | ISO | Japan | China | |||||||||
| Standard | Grade (UNS) | Standard | Steel Name (Steel Number) | Standard | Grade (Steel Number) | Standard | Grade (Steel Number) | Standard | Grade | Standard | Grade | Standard | Grade | ||
| AISI SAE; ASTM A240/A240M; A276/A276M | AISI 304 (UNS S30400) | EN 10088-2; EN 10088-3 | X5CrNi18-10 (1.4301) | DIN EN 10088-2; DIN 17440 | X5CrNi18-10 (1.4301) | DIN EN 10088-2; BS970 :1996 | X5CrNi18-10 (1.4301); 304S15 | ISO 15510 | X5CrNi18-10 | JIS G4304 | SUS304 | GB/T 1220; GB/T 3280 | 06Cr19Ni10; 0Cr18Ni9 (Old designation) | ||